Technical SEO focuses on optimizing your website to ensure search engines can easily find, understand, and index your content. It also includes enhancing user experience by improving site speed and mobile usability. Effective technical SEO can significantly increase your visibility in search results.
In this post, we’ll cover the fundamentals and best practices for optimizing your website for technical SEO.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Technical SEO is crucial for your SEO performance. If your site’s pages aren’t accessible to search engines, they won’t appear in search results, regardless of the quality of your content. This can lead to a significant loss of traffic and potential revenue.
Additionally, website speed and mobile-friendliness are confirmed ranking factors. Slow-loading pages can frustrate users, leading them to leave your site, which can indicate a poor user experience to search engines and negatively impact your rankings.
To grasp technical SEO more thoroughly, it’s essential to understand two key processes: crawling and indexing.
What Is Crawling and How to Optimize for It?
Crawling is a crucial part of how search engines operate.
When search engines crawl, they follow links on known pages to discover new ones.
For instance, whenever we publish new blog posts, we add them to our main blog page. The next time a search engine like Google crawls our blog page, it finds the newly added links to our latest posts.
This is one way Google discovers our new content.
To ensure your pages are accessible to search engines, consider these strategies:
How does crawling work?
Crawling is the process where search engines extract content from webpages and follow links to discover additional pages. There are several methods to control what content search engines crawl on your site. Here are some options:
Robots.txt:
A robots.txt file specifies which areas of your site search engines are allowed to access and which ones they should avoid.
Crawl Rate:
While there’s a crawl-delay directive in robots.txt supported by many crawlers, Google doesn’t adhere to this. To adjust Google’s crawl rate, you’ll need to use Google Search Console.
Access Restrictions:
If you want to restrict access to certain pages from search engines but still allow access to specific users, consider these options:
- Implement a login system
- Use HTTP authentication requiring a password for access
- Employ IP whitelisting to permit access only from specific IP addresses
These access restrictions are useful for scenarios like internal networks, member-only content, or staging and development sites. They enable a select group of users to access the pages while preventing search engines from indexing them.
How to see Google’s crawl activity?
To monitor Google’s crawling activity on your website, utilize the “Crawl stats” report within Google Search Console. This report provides detailed insights into how Google is crawling your site.
For a comprehensive view of all crawl activity, access your server logs and consider using tools for deeper analysis. Some hosting control panels like cPanel offer access to raw logs and aggregators such as AWstats and Webalizer.
What Are Crawl adjustments?
Crawl adjustments are necessary as each website has a unique crawl budget, determined by how frequently Google intends to crawl the site and the site’s crawlability. Pages that are popular or frequently updated will be crawled more frequently, while less popular or poorly linked pages may be crawled less often.
If crawlers encounter difficulties while crawling your site, they may reduce or halt crawling until conditions improve.
Following crawling, pages are rendered and added to the index, which serves as the master list of pages eligible to appear in search results.
Create an SEO-Friendly Site Architecture
Site architecture, or site structure, refers to the way pages are interconnected within your website.
An effective site structure organizes pages so that crawlers can quickly and easily find your content. Ensure all pages are just a few clicks away from your homepage.
The homepage should link to the category pages, and category pages link to individual subpages.
This setup minimizes the number of orphan pages—pages with no internal links pointing to them, which makes them hard for crawlers and users to find.
If you use Semrush, you can easily identify orphan pages on your site.
Set up a project in the Site Audit tool and crawl your website.
After the crawl is complete, go to the “Issues” tab and search for “orphan.”
The tool will indicate if your site has orphan pages.
To resolve this issue, add internal links on non-orphan pages that point to the orphan pages.
Submit Your Sitemap to Google
Using an XML sitemap can help Google discover your webpages.
An XML sitemap is a file that lists important pages on your site, guiding search engines to locate and index them.
Here is a screenshot of what a sitemap looks like:
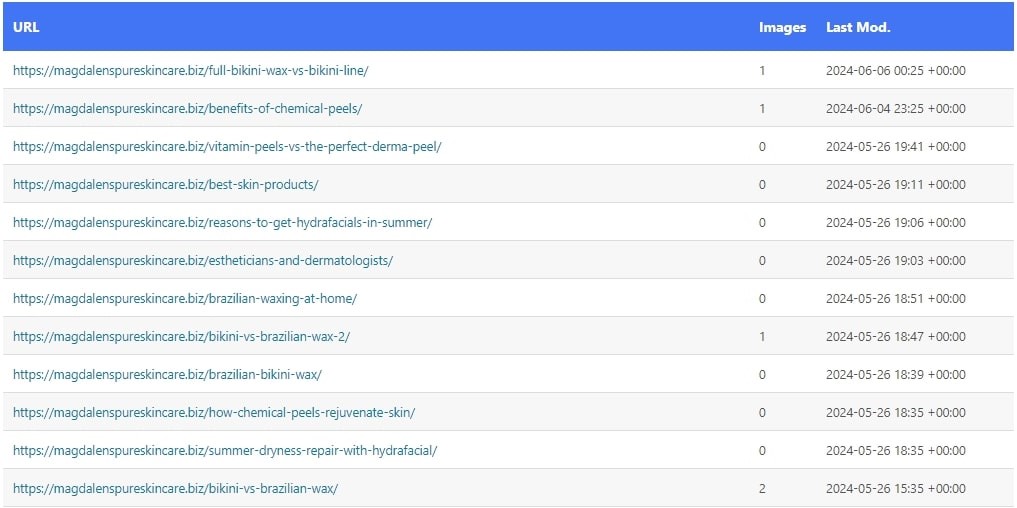
This is particularly useful for large sites or sites with poorly interlinked pages.
Your sitemap is typically found at one of these URLs:
– yoursite.com/sitemap.xml
– yoursite.com/sitemap_index.xml
Once you locate your sitemap, submit it to Google through Google Search Console (GSC).
In GSC, navigate to ‘Indexing’ > ‘Sitemaps’ from the sidebar.
After Google processes your sitemap, you’ll receive a confirmation message like this:

Now, comes the 2nd part which is Indexing. Let’s learn about it and see how it works.
What Is Indexing and How to do its Optimization?
After search engines crawl your pages, they analyze and understand the content before storing it in their search index, a massive database of billions of web pages.
For your pages to appear in search results, they must be indexed by search engines.
To check if your pages are indexed, use a ‘site:’ operator search. For instance, to check the index status of magdalenspureskincare.biz, type ‘site:magdalenspureskincare.biz’ into Google’s search box. This will give you an approximate number of indexed pages.
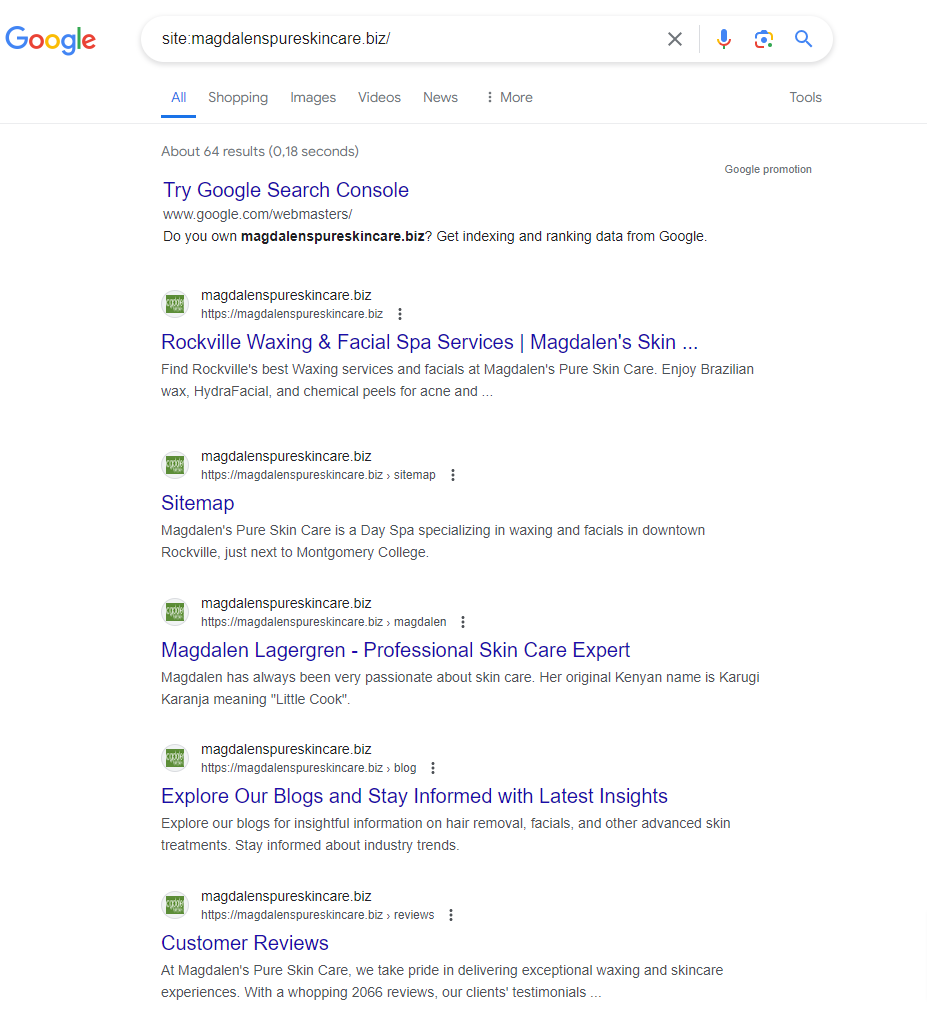
Google displays around 64 results for ‘site:www.magdalenspureskincare.biz’
You can also verify the index status of individual pages by searching the page URL with the ‘site:’ operator.
For example:
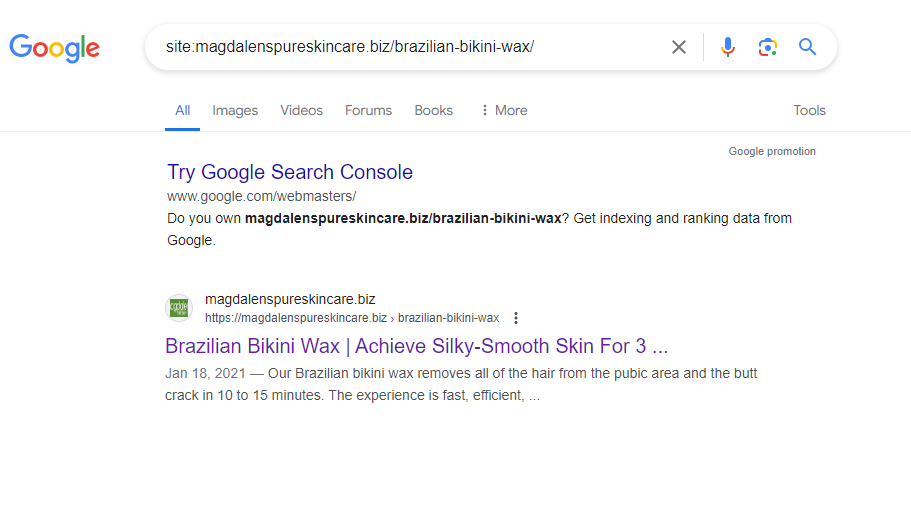
To ensure Google can index your web pages without issues, consider the following steps:
Use the Noindex Tag Carefully
The ‘noindex’ tag is an HTML snippet that prevents your pages from being indexed by Google.
Placed within the <head> section of your webpage, it looks like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
You should aim to have all important pages indexed, using the ‘noindex’ tag only to exclude specific pages from indexing, such as:
– Thank you pages
– PPC landing pages
Implement Canonical Tags Where Needed
When Google encounters similar content on multiple pages of your site, it can struggle to determine which page to index and display in search results.
This is where ‘canonical’ tags are useful.
The canonical tag (rel=”canonical”) designates a link as the original version, guiding Google on which page to index and rank.
This tag should be placed within the <head> section of duplicate pages (and it’s beneficial to use it on the main page too) and looks like this:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”URL-of-the-original-page”>
Technical SEO Best Practices
Building an SEO-friendly site structure, submitting your sitemap to Google, and appropriately using no index and canonical tags will help ensure your pages are crawled and indexed.
However, to fully optimize your website for technical SEO, consider implementing these additional best practices.
Use HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, offering enhanced protection for sensitive user data like passwords and credit card details.
Since 2014, HTTPS has been a ranking signal, influencing search engine rankings.
To check if your site is using HTTPS, simply visit it and look for the lock icon in the browser bar.
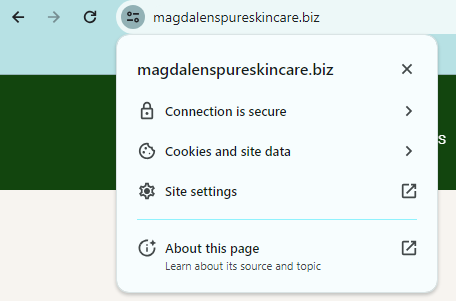
If you see a “Not secure” warning, your site isn’t using HTTPS, and you’ll need to install an SSL/TLS certificate.
This certificate authenticates the website’s identity and ensures a secure connection for users.
You can obtain a free SSL/TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt.
Find & Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content occurs when you have identical or very similar content across multiple pages on your website.
For instance, the website Buffer had these two URLs with nearly identical content:
– https://buffer.com/resources/social-media-manager-checklist/
– https://buffer.com/library/social-media-manager-checklist/
Google doesn’t penalize websites for duplicate content, but it can lead to issues such as:
– Unwanted URLs ranking in search results
– Dilution of backlinks
– Wastage of crawl budget
With SEMrush’s Site Audit tool, you can identify duplicate content issues on your site.
Start by performing a full crawl of your site and then navigate to the “Issues” tab.
In the “Issues” tab, search for “duplicate content.” The tool will highlight any errors and provide guidance on how to resolve them when you click on “Why and how to fix it.”
Make Sure There Is Only One Version of Your Website, Accessible to Users and Crawlers
For optimal SEO performance, ensure that users and crawlers can only access one version of your site:
– https://yourwebsite.com
– https://www.yourwebsite.com
Having both versions accessible can lead to duplicate content problems and diminish the impact of your backlink profile. Some sites may link to the www version while others link to the non-www version, causing potential issues with Google rankings.
To mitigate this, choose one version of your website and implement a redirect from the other version to your primary site. This helps streamline your site’s structure and improves SEO consistency.
Optimize Your Page Speed
Page speed significantly impacts your website’s ranking, both on mobile and desktop devices. Aim to optimize your site’s loading time for better performance.
Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool is a valuable resource to evaluate your website’s speed, providing a performance score ranging from 0 to 100. A higher score indicates better performance.
Consider these strategies to enhance your website speed:
- Compress images: Images often constitute the largest files on a webpage. Utilize image optimization tools to compress images, reducing file sizes and enhancing loading times.
- Implement a content distribution network (CDN): A CDN stores copies of your web pages on servers worldwide and directs visitors to the nearest server. This minimizes the distance for requested files to travel, improving loading speed.
- Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files: Minification eliminates unnecessary characters and whitespace from code, reducing file sizes and enhancing page load times.
Make Your Website Is Mobile-Friendly
Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily assesses the mobile versions of webpages for indexing and ranking.
Ensure your website is mobile-friendly to align with this approach.
To evaluate your site’s mobile compatibility, utilize the PageSpeed Insights tool. After analyzing a webpage, navigate to the “SEO” section and review the “Passed Audits” section.
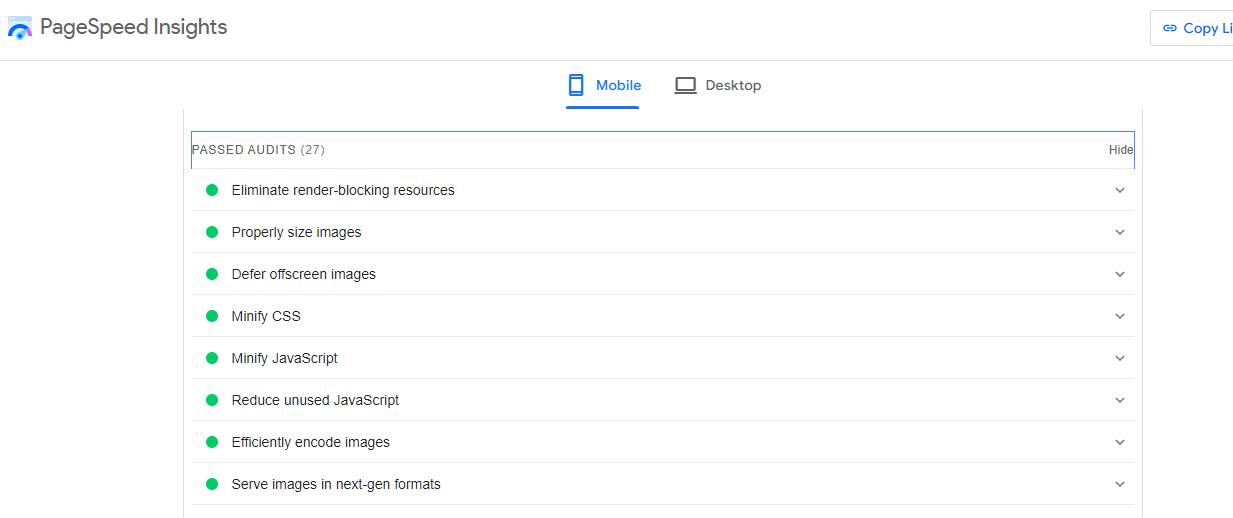
Look for indicators of mobile-friendly elements, including:
- Meta viewport tags: Code instructing browsers on how to manage page sizing for the visible area.
- Legible font sizes.
- Sufficient spacing around buttons and clickable elements.
By addressing these factors, you optimize your website for mobile devices, enhancing its visibility and performance in search results.
Use Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation, also known as “breadcrumbs,” is a series of text links that guide users through the hierarchical structure of a website, indicating their current location and the path they followed to reach it.
Implementing breadcrumbs on your website enhances site navigation, particularly beneficial for large sites like ecommerce platforms.
Breadcrumbs simplify navigation by allowing users to easily access higher-level pages without the hassle of using the back button or navigating through complex menus.
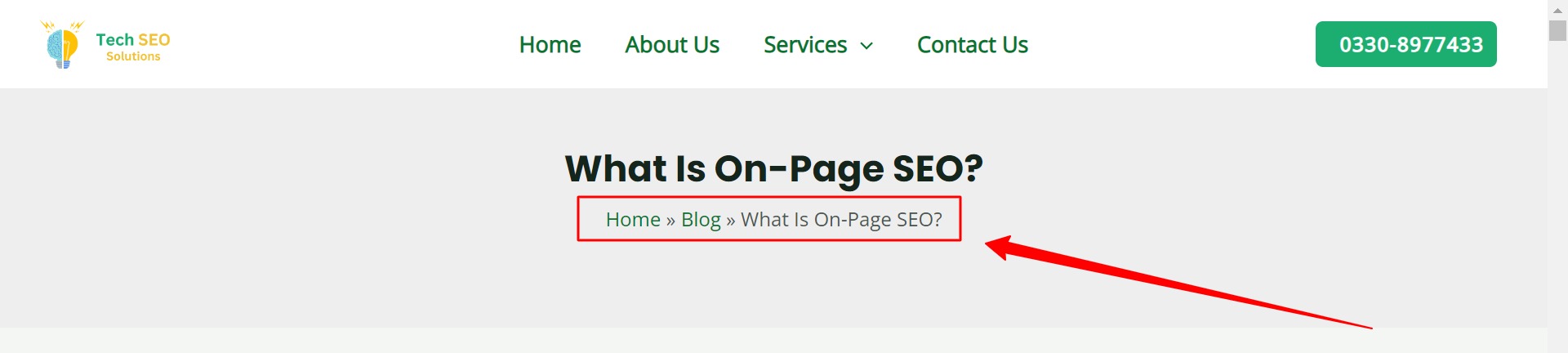
From an SEO perspective, breadcrumbs play a crucial role by distributing link equity (PageRank) throughout your site, ultimately aiding in higher search engine rankings.
For WordPress or Shopify websites, implementing breadcrumb navigation is straightforward. Some themes may include breadcrumbs by default, but if not, you can easily set them up using the Yoast SEO plugin, ensuring seamless navigation and enhanced SEO performance.
Use Pagination
Pagination is a navigation method commonly employed to break down lengthy content lists into multiple pages, such as on our blog.
Unlike infinite scrolling, where content dynamically loads as users scroll down, pagination presents all content upfront. This approach is preferred because it ensures accessibility for search engines like Google.
Infinite scrolling can pose indexing challenges for Google, potentially hindering access to dynamically loaded content and consequently impacting search visibility.
Properly implemented pagination includes links to subsequent pages, allowing Google to efficiently discover and index your content, thus enhancing its visibility in search results.
Review Your Robots.txt File
A robots.txt file directs search engines on which areas of your site to crawl and which to avoid.
You can find your robots.txt file at your homepage URL with “/robots.txt” appended to it, such as yoursite.com/robots.txt.
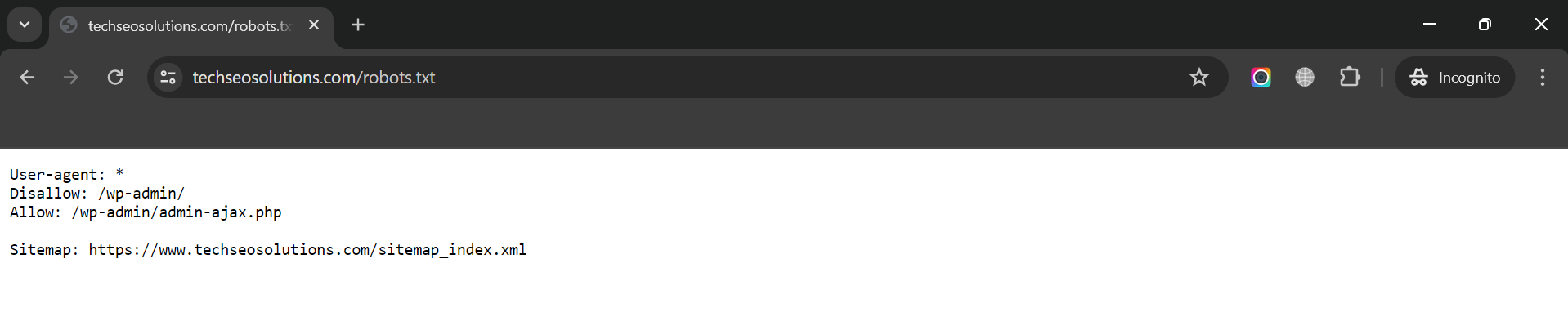
Review this file to prevent accidentally blocking access to critical pages that Google should crawl.
For instance, ensure you haven’t disallowed access to essential pages like blog posts or standard website pages, as this could prevent them from appearing in Google search results.
Implement Structured Data
Structured data, also known as schema markup, is code designed to help Google comprehend a webpage’s content more effectively.
By incorporating appropriate structured data, your pages have the potential to feature rich snippets in search results.
Rich snippets enhance search listings by displaying additional information beneath the title and description, making your pages more enticing and potentially increasing click-through rates (CTR).
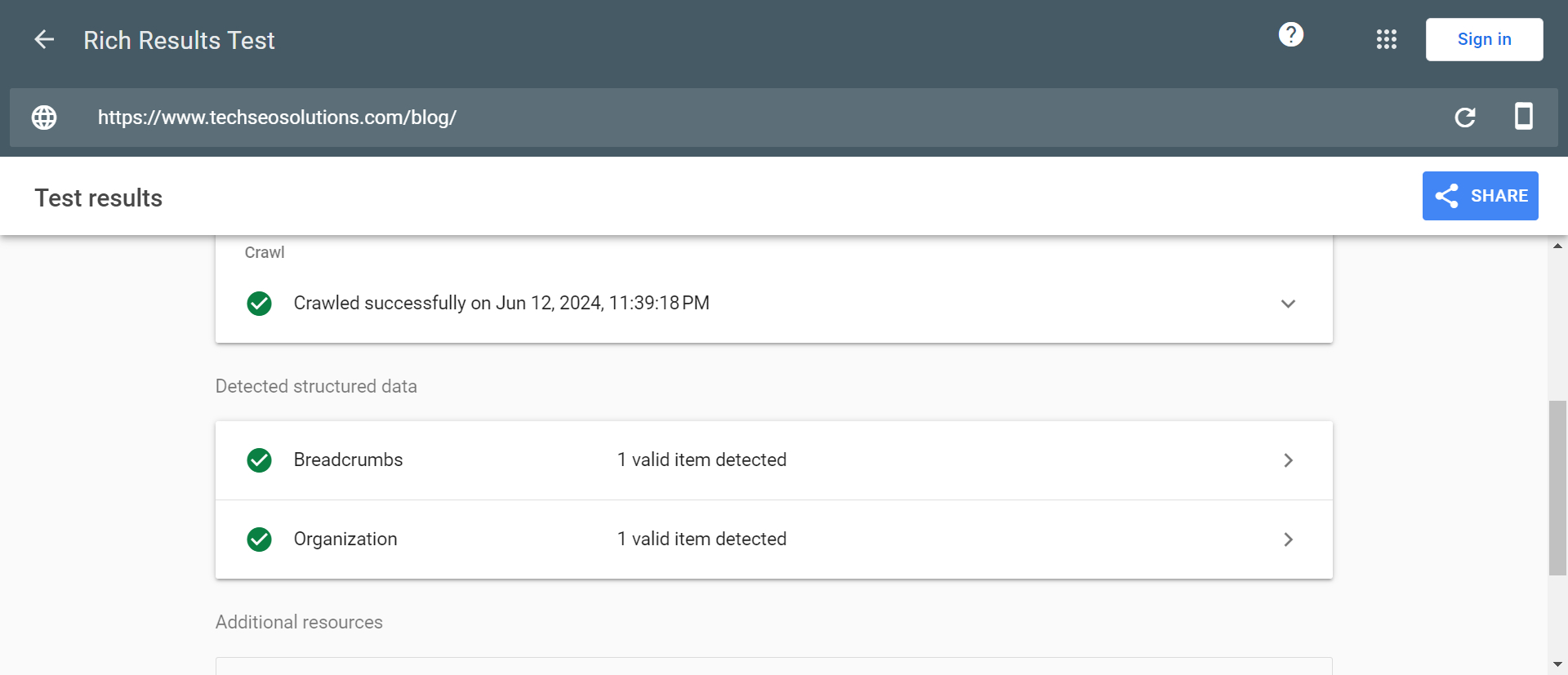
Google supports numerous structured data markups, so select the one that best aligns with your page content. For instance, ecommerce stores may benefit from adding product structured data to their product pages.
To simplify the process, utilize free structured data generator tools or plugins like Yoast SEO for WordPress, which streamline the implementation of structured data without manual coding.
Find & Fix Broken Pages
Having broken pages on your website can harm user experience and waste potential backlinks if they point to non-existent resources.
To identify broken pages, utilize SEMrush’s Site Audit tool by crawling your site and checking the “Issues” tab for “4xx” errors.
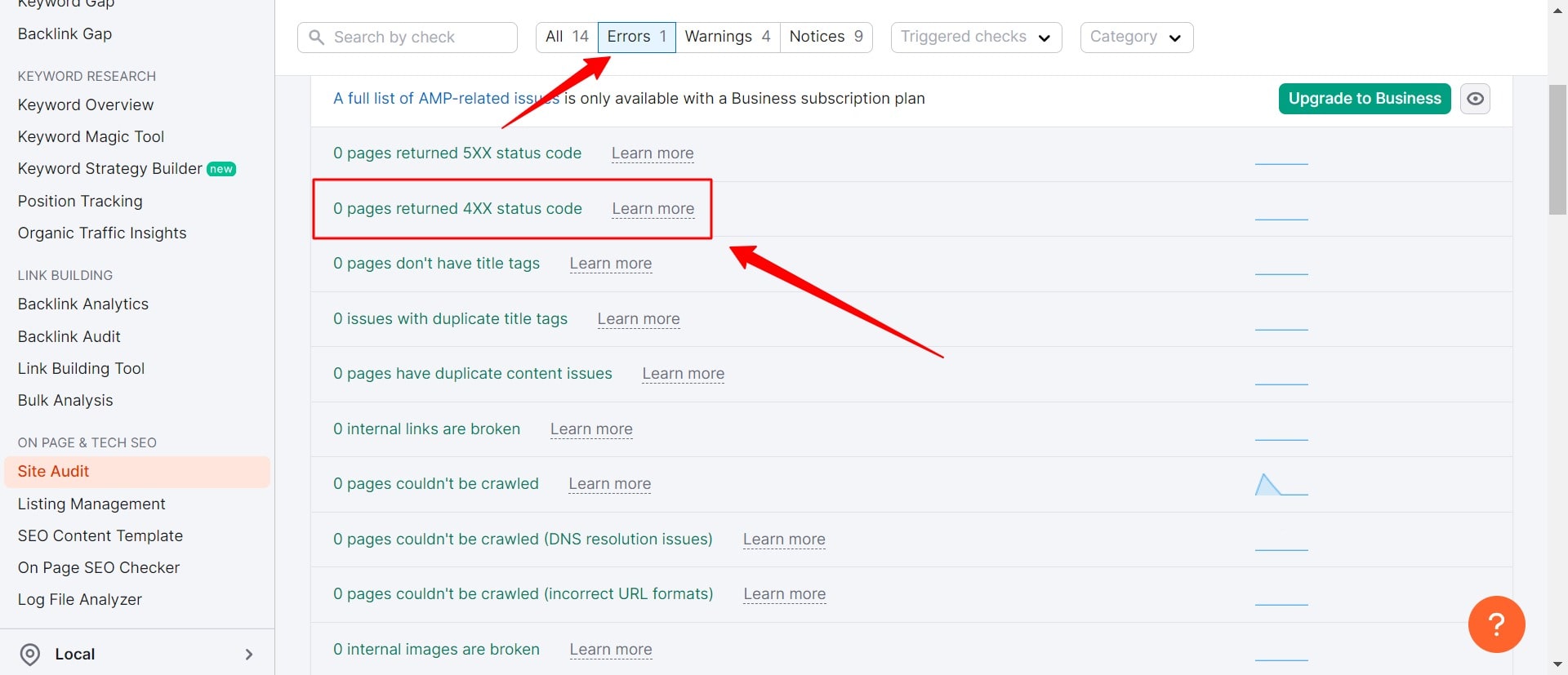
Once identified, you have two options to address broken pages:
- Restore accidentally deleted pages.
- Redirect obsolete pages to relevant alternatives on your site.
After fixing broken pages, review and update internal links pointing to them. Use the Site Audit tool to search for “internal links” in the “Issues” tab to identify broken internal links. Then, update these links to direct users to the correct pages.
Optimize for the Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals are crucial speed metrics utilized by Google to assess user experience on websites.
These metrics consist of:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time taken for a webpage to load its largest element.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): It is a metric used to assess the responsiveness of a webpage. It utilizes data from the Event Timing API to measure the latency associated with user interactions on the page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Assesses the unexpected shifts in layout elements on a webpage.
To ensure your website meets the Core Web Vitals standards, target the following scores:
- LCP: 2.5 seconds or less
- INP: 200 milliseconds or less
- CLS: 0.1 or less
You can evaluate your website’s performance for Core Web Vitals metrics using Google Search Console’s “Core Web Vitals” report.
Use Hreflang for Content in Multiple Languages
If your website has content available in multiple languages, it’s crucial to utilize hreflang tags.
Hreflang tags are HTML attributes used to specify the language and geographical targeting of a webpage, assisting Google in delivering the correct versions of your pages to users.
For instance, if you offer your homepage in various languages like English and Spanish, each version should incorporate hreflang tags to inform Google about the intended audience.
Implementing hreflang tags is straightforward. Simply include the relevant hreflang tags within the <head> section of all versions of your pages.
Let’s say, you want to present your homepage in 3 different languages, English, portuguese and Spanish. These are the tags that you will use:
- <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”x-default” href=”https://yourwebsite.com” />
- <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”es” href=”https://yourwebsite.com/es/” />
- <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”pt” href=”https://yourwebsite.com/pt/” />
- <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en” href=”https://yourwebsite.com” />
Fix HTTP Errors
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol, but what’s crucial is understanding HTTP errors and how they impact both users and search engines.
HTTP errors can hinder search bots from accessing key content on your site, making it essential to resolve these errors promptly and effectively.
Each HTTP error is unique and demands a specific solution. Below, we briefly explain each error, with links provided for more detailed resolutions.
- 301 Permanent Redirects: Used to permanently redirect traffic from one URL to another. While your CMS can set these up, too many redirects can slow down your site and degrade user experience. Aim for zero redirect chains, as excessive redirects can cause search engines to abandon crawling that page.
- 302 Temporary Redirects: Temporarily redirects traffic from a URL to a different webpage. While users are sent to the new webpage, the cached title tag, URL, and description remain consistent with the origin URL. If the temporary redirect remains long enough, it will eventually be treated as a permanent redirect.
- 403 Forbidden Messages: Indicate that the requested content is restricted based on access permissions or server misconfiguration.
- 404 Error Pages: Inform users that the requested page doesn’t exist, either due to removal or a wrong URL. It’s beneficial to create engaging, on-brand 404 pages to retain visitors on your site.
- 405 Method Not Allowed: Means the server recognized but blocked the access method, resulting in an error message.
- 500 Internal Server Error: A general error indicating your server is experiencing issues delivering your site to the requesting party.
- 502 Bad Gateway Error: Occurs due to miscommunication or invalid response between website servers.
- 503 Service Unavailable: Indicates the server is functioning properly but is unable to fulfill the request.
- 504 Gateway Timeout: Means a server did not receive a timely response from your web server to access the requested information.
Addressing these errors is vital to maintaining a positive experience for both users and search engines, ensuring they continue to return to your site.
Even if your site has been crawled and indexed, accessibility issues that block users and bots will impact your SEO. With that in mind, let’s move on to the next stage of your technical SEO audit — renderability.
Rendering
Ensuring your site is accessible depends on its ease of rendering. Here are the key website elements to review for your renderability audit.
Server Performance
As discussed earlier, server timeouts and errors can lead to HTTP issues that prevent users and search bots from accessing your site. If you detect server problems, promptly resolve them. Ignoring these issues can lead to search engines removing your webpage from their index, as displaying a broken page provides a poor user experience.
HTTP Status
Like server performance issues, HTTP errors can block access to your webpages. To conduct a thorough error audit of your site, utilize a web crawler such as Screaming Frog, Botify, or DeepCrawl.
Load Time and Page Size
If your page takes too long to load, a high bounce rate isn’t your only concern. Slow loading times can cause server errors that block bots from accessing your webpages or lead to them crawling partially loaded pages missing critical content. The more demand there is for a resource, the more resources bots will spend trying to load, render, and index pages. To optimize for SEO, you should focus on reducing your page load time.
JavaScript Rendering
Google has acknowledged that processing JavaScript (JS) is a challenging task. To improve accessibility, it recommends using pre-rendered content. Google also provides numerous resources to help you understand how search bots interact with JS on your site and how to address search-related issues.
Page Depth
Page depth refers to the number of layers a page is from your homepage, or how many clicks it takes to reach it. Maintaining a shallow site architecture is ideal, but it should also be intuitive and well-organized. While sometimes a multi-layered structure is unavoidable, it’s crucial to keep essential pages, such as product and contact pages, no more than three clicks deep. Burying important pages too deep within your site makes them less accessible and negatively impacts user and bot experience.
Redirect Chains
When you implement redirects, you’re trading off crawl efficiency. Redirects can slow down crawling, reduce page load speed, and even make your site inaccessible if not configured correctly. Therefore, it’s best to minimize the use of redirects. Once you’ve resolved accessibility issues, you can focus on optimizing how your pages rank in the SERPs.
Top Technical SEO tools
Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools) is a free service from Google that enables you to monitor and troubleshoot your website’s performance in search results. Utilize it to identify and resolve technical errors, submit sitemaps, review structured data issues, and more. Bing and Yandex offer their own equivalent tools for similar insights.
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test evaluates how easily users can interact with your page on a mobile device and highlights specific issues, such as small text sizes or incompatible plugins. The test displays what Google sees when crawling the page. Additionally, use the Rich Results Test to view the content Google detects for both desktop and mobile devices.
Chrome DevTools
Chrome DevTools serves as Chrome’s integrated webpage debugging tool. It’s invaluable for diagnosing page speed problems, enhancing web page rendering performance, and addressing various technical SEO issues. It has many uses from a technical SEO perspective.
PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed Insights assesses the loading speed of your webpages, providing not only a performance score but also actionable suggestions to enhance loading times.
Ahrefs
Site Audit tool by Ahrefs is an essential tool for technical SEO, designed to crawl all the pages on your website and deliver a comprehensive SEO health score. It visualizes critical data with charts, identifies all potential SEO issues, and offers actionable recommendations for improvement.
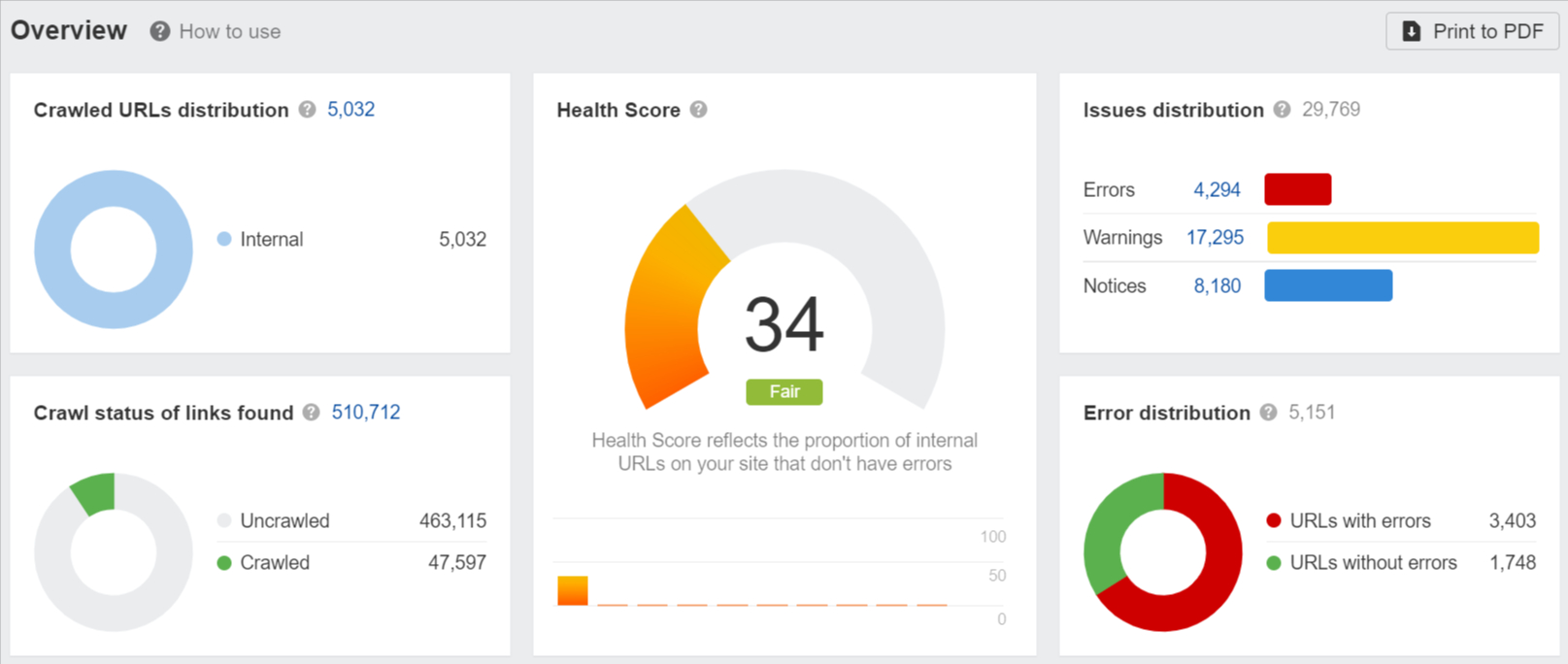
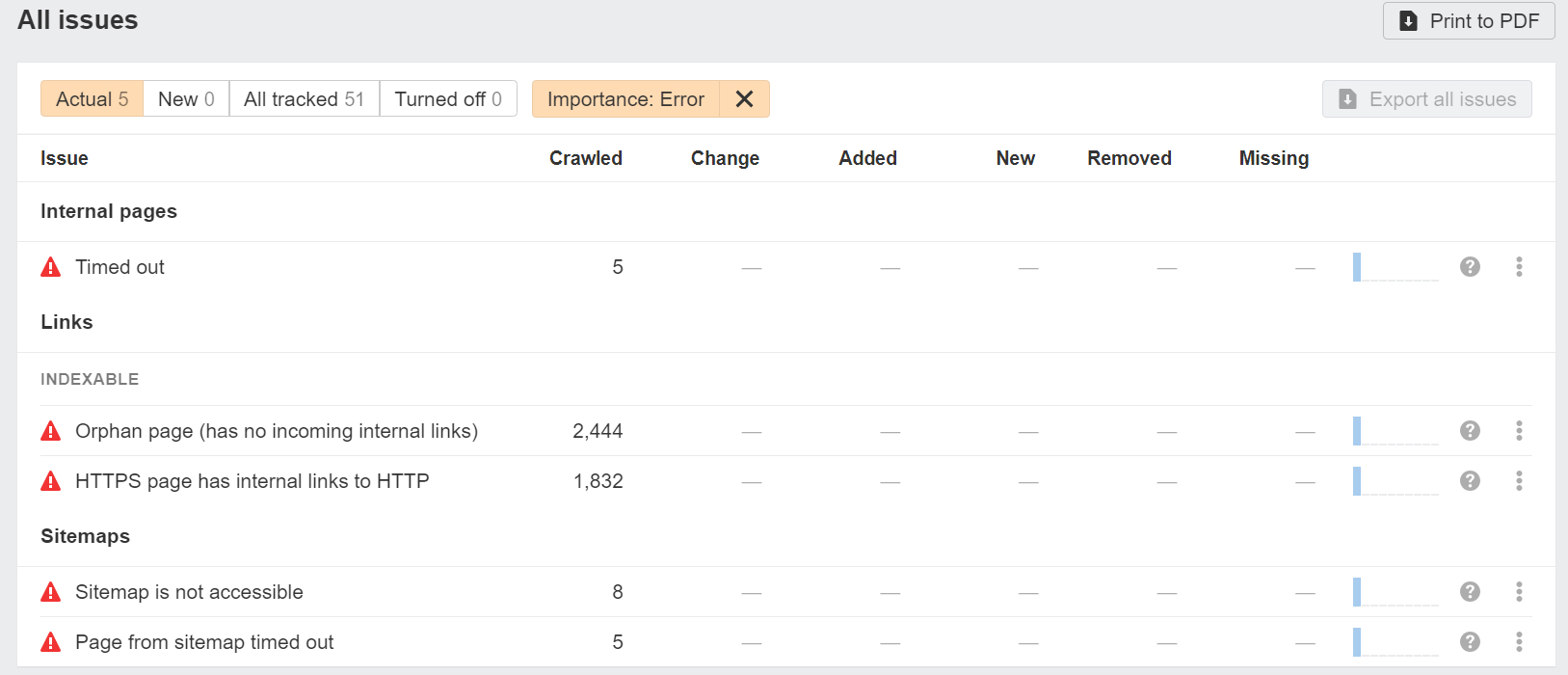
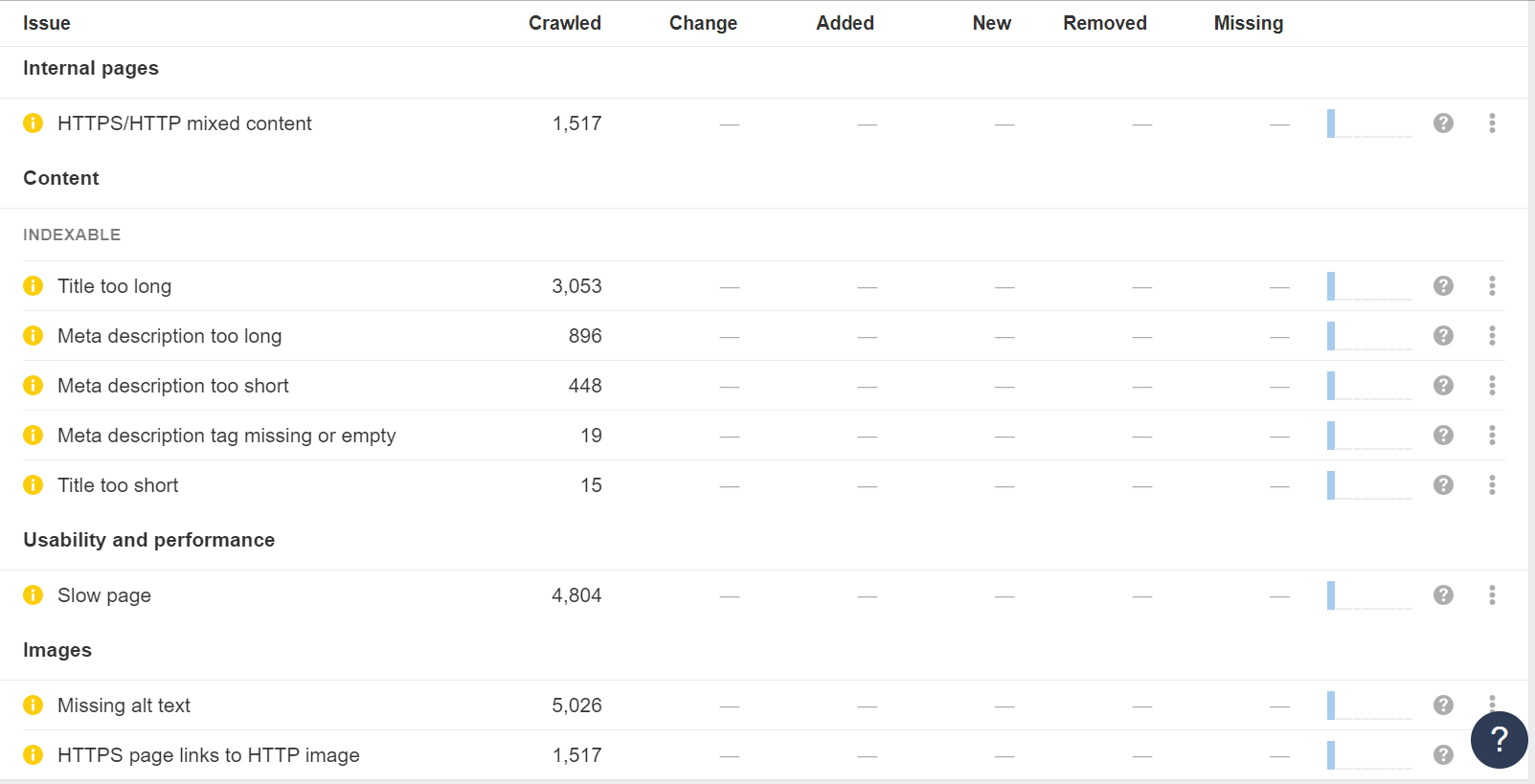
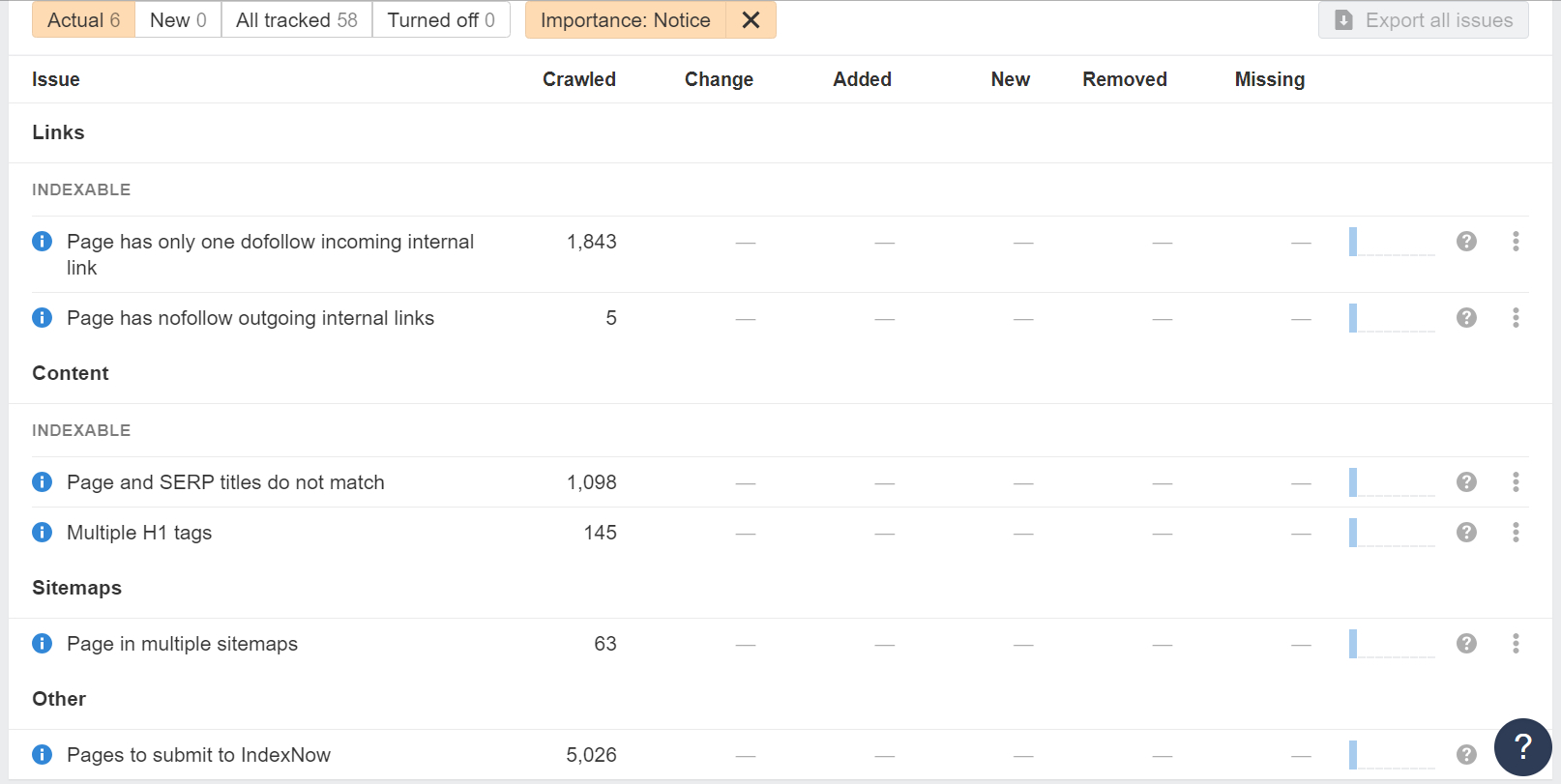
Whether you have a small site or a massive one, Site Audit can handle it. You can expedite the crawling process by verifying your domain and adjusting the speed settings. Additionally, you can optimize the crawl by excluding or including specific sections of your site, ensuring efficient and relevant analysis.
SEMrush
The Site Audit tool by SEMrush is an indispensable asset for technical SEO, meticulously designed to crawl every page of your website and provide a thorough SEO health score. This tool visualizes crucial data with intuitive charts, identifies all potential SEO issues, and delivers actionable recommendations for enhancement.
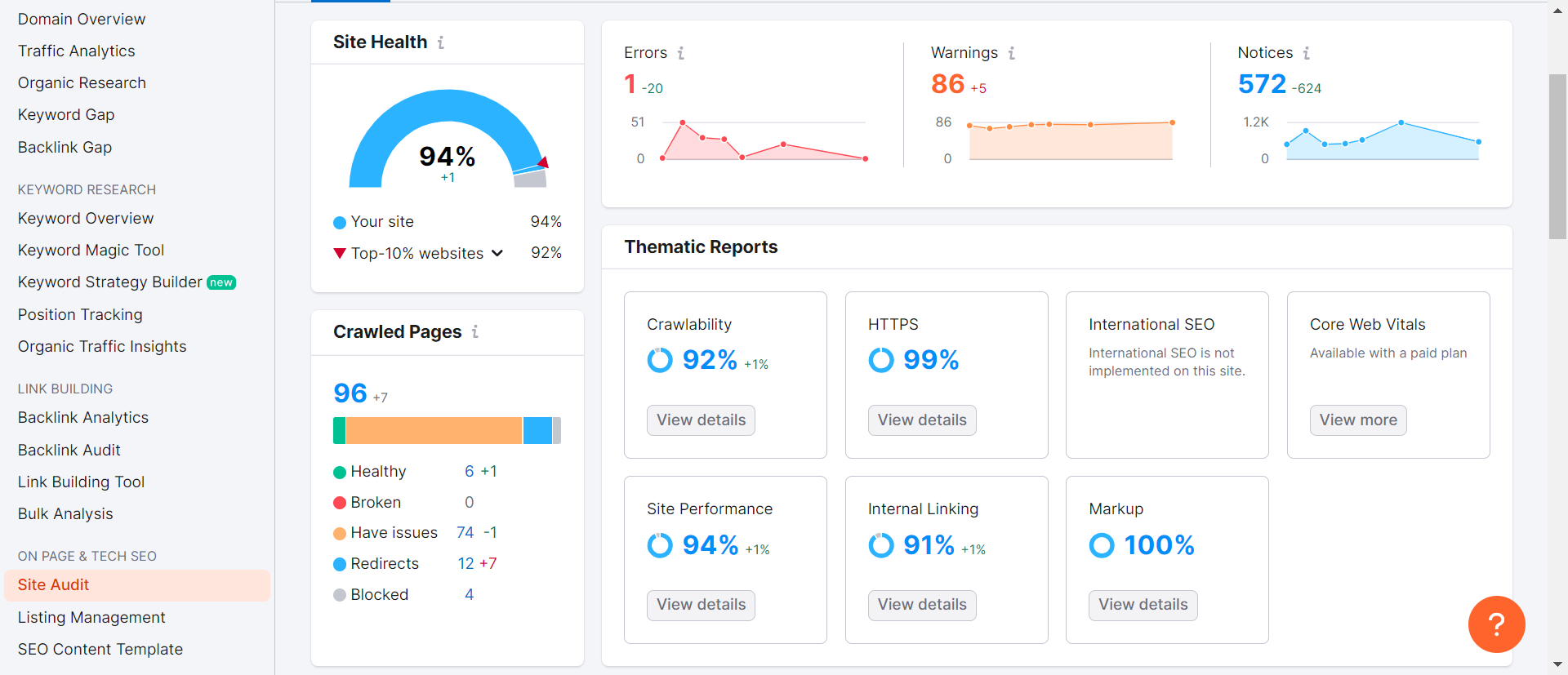
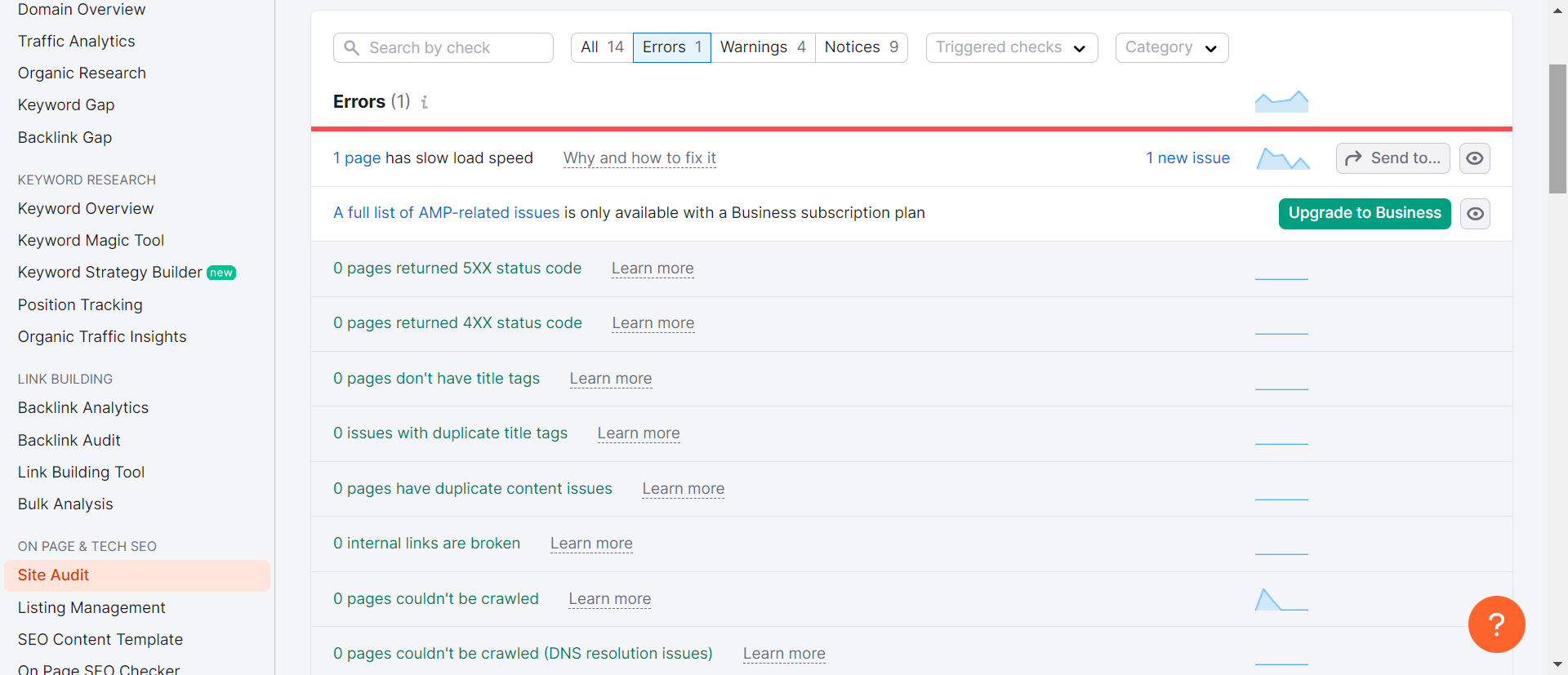
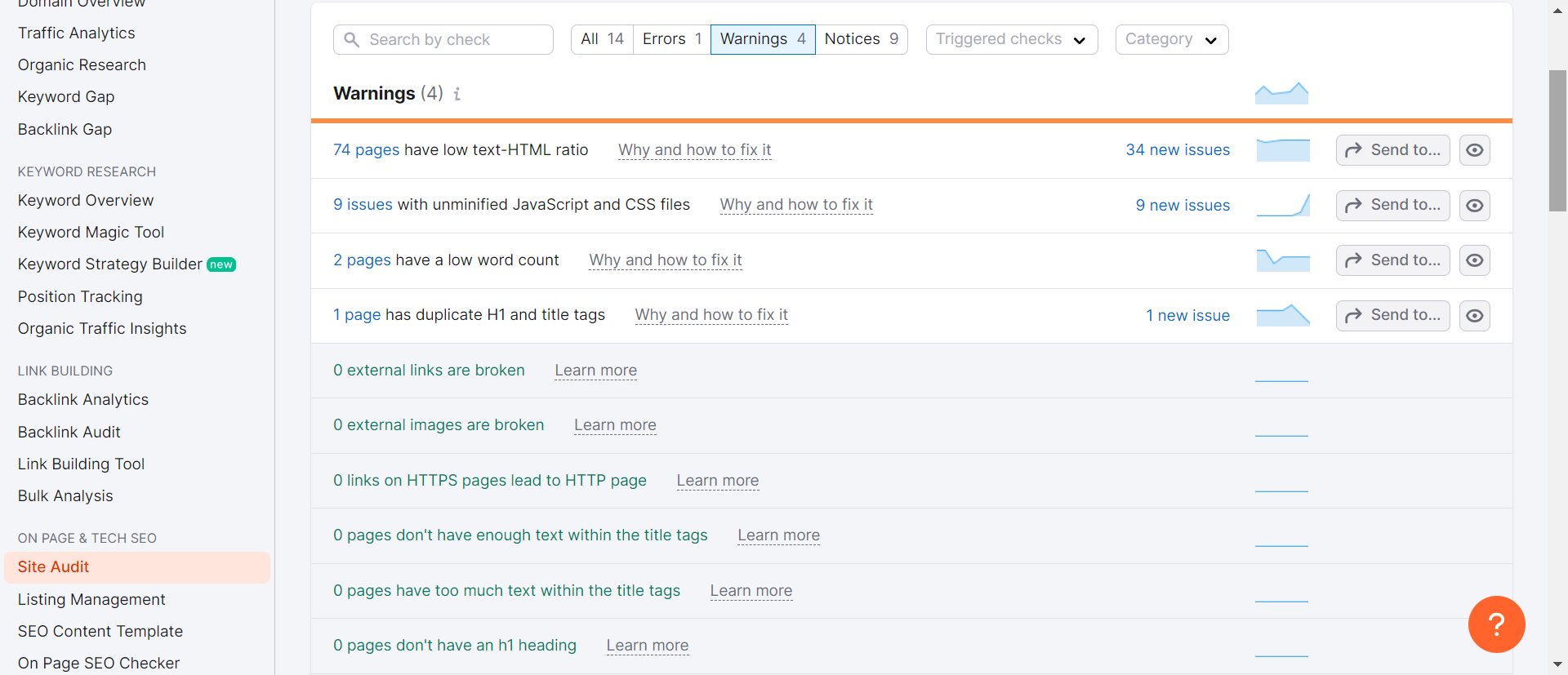
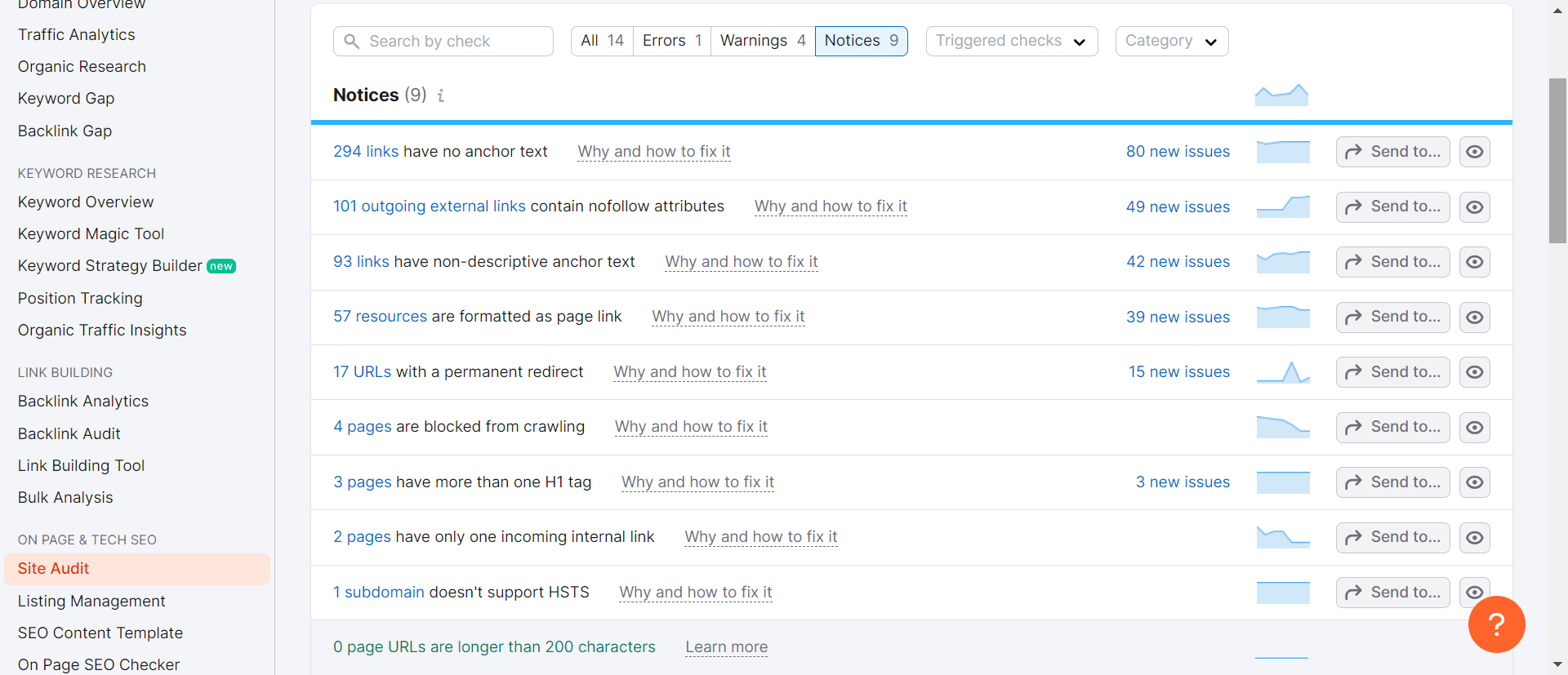
Regardless of whether you operate a small website or a vast one, the Site Audit tool can manage it effectively. You can speed up the crawling process by verifying your domain and adjusting the crawl speed settings. Moreover, you can tailor the crawl by including or excluding specific sections of your site, ensuring an efficient and targeted analysis.
Conclusion
Technical optimization isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. As your website evolves, new issues may arise, underscoring the importance of regularly monitoring your technical SEO health and promptly addressing any issues that surface.
Redirect chains and loops can significantly harm SEO by creating a poor user experience. Without a comprehensive crawl-based audit, such issues may go unnoticed.
Regular technical SEO audits provide actionable insights to enhance search performance and ensure a smooth user experience.
Technical SEO serves as the foundation of an effective SEO strategy. By optimizing your website’s infrastructure and resolving obstacles that hinder crawling and indexing, technical SEO paves the way for successful content creation and link-building efforts.
In conclusion, prioritizing technical SEO ensures your website remains optimized for search engines and sets the stage for ongoing SEO success.




