On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, involves optimizing webpages and their content to appeal to both search engines and users. This process is crucial for improving your site’s ranking on Google and increasing organic traffic.
Key tasks in on-page SEO include optimizing for search intent, refining title tags, enhancing internal links, and structuring URLs effectively.
In this guide, we’ll explore various techniques to optimize your site for on-page SEO considerations. But, let’s first clarify the distinction between on-page SEO and off-page SEO:
Table of Contents
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
On-page SEO encompasses all the actions you can take directly on your webpage (internally) to enhance your rankings. This includes optimizing content, meta tags, and internal linking.
Off-page SEO involves optimization efforts outside your website (externally) aimed at boosting your rankings. Backlinks are the most significant off-page SEO factor, but it also includes activities like social media engagement and public relations.
Both on-page and off-page SEO are crucial components of a comprehensive SEO strategy. However, you have more control over on-page SEO elements, making it a great starting point for improving your site’s performance.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
Search engines rely on keywords and other on-page SEO elements to determine if a page aligns with a user’s search intent. If the page is relevant and helpful, Google will display it to the user.
Simply put:
Google considers on-page SEO signals when ranking pages.
Although the Google algorithm constantly evolves, it consistently prioritizes user experience. Google advises focusing on “people-first content,” which means creating valuable content that meets user intent is more crucial than ever.
Let’s dive into how you can update your content to align with on-page SEO best practices.
9 On-Page SEO Techniques for Your Website
Here are some essential on-page optimization techniques to consider:
- Write unique and helpful content
- Place target keywords strategically in the content
- Craft keyword-rich title tags
- Create click-worthy meta descriptions
- Use headings and subheadings to structure your page
- Optimize URLs
- Add internal links
- Include external links
- Incorporate and optimize images
Let’s explore each of these in more detail.
Write Unique and Helpful Content
One of the most crucial on-site SEO steps is creating high-quality content that aligns with your readers’ search intent.
Begin by conducting keyword research to identify relevant topics and target keywords.
While targeting high search volume keywords can be beneficial, also consider the keyword difficulty (KD %). High KD % scores indicate more competitive keywords, which are harder to rank for.
Additionally, focus on less competitive long-tail keywords. They often have lower search volumes and KD %, making them easier to rank for.
After selecting your keywords, it’s time to create your content.
Here are some best practices for crafting optimized, high-quality content:
- Incorporate keywords naturally into your content (avoid keyword stuffing)
- Match the search intent of your target keyword
- Fully answer the query—ensure your content is useful to users
- Write unique content that offers something competitors don’t
- Include visual content (more on that later)
Place Target Keywords Strategically
Now that you have your target keywords, it’s time to strategically place them within your content.
Google scans your content to understand the page’s topic, and readers do the same.
Include your target keywords in these key areas:
H1 (Main Heading)
First Paragraph
Subheaders (H2s, H3s, etc.)
This approach helps Google understand the context of your page, and allows users to quickly determine if the content matches their search intent.
Write Keyword-Rich Title Tags
Title tags are pieces of HTML code that define the title of a webpage. They appear in search engine results, social media posts, and browser tabs.
Moreover, they can influence whether users click on your page.
On the SERP (search engine results page), title tags look like this:
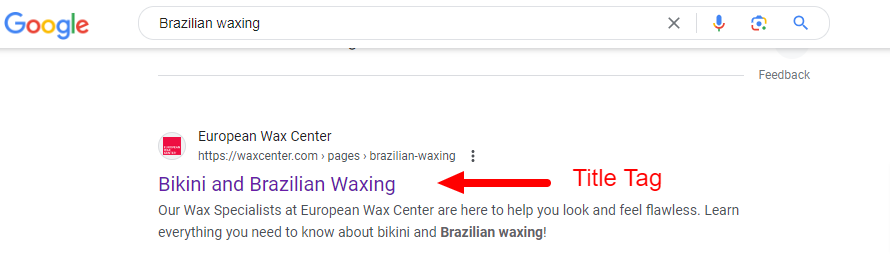
A title tag on SERP might read “What is a Title Tag & How to Optimize Your Title Tags for SEO”
Here are some tips for writing effective title tags:
Keep it brief
Aim for 50-60 characters to prevent Google from truncating them.
Include your target keyword
This helps Google and users understand your page’s topic.
Be unique
Avoid duplicate title tags to ensure each page’s purpose is clear to Google and users.
Write Click-Worthy Meta Descriptions
A meta description tag is an HTML element that offers a brief summary of a webpage. Search engines like Google often use it to generate the snippet, which is the descriptive text part of a search result.
Typically, it appears on the SERP below your page’s title, like this:
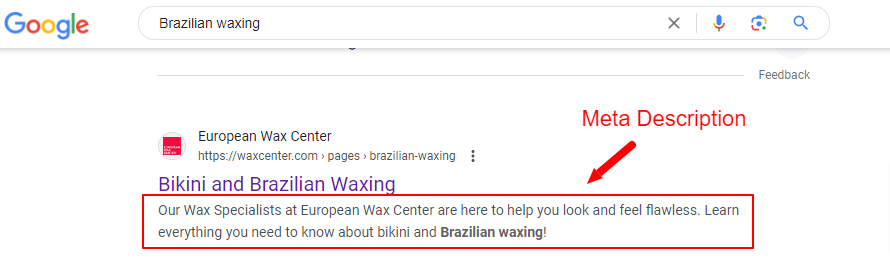
Meta descriptions don’t directly affect Google rankings. However, like title tags, they can influence whether a user clicks on your page or another, potentially driving more search traffic.
If your meta description doesn’t match the user’s search intent or the content on the page, Google may create its own description for the SERP.
To increase the likelihood of Google using your chosen meta description, follow these best practices:
Keep in mind mobile devices: Google truncates meta descriptions after about 120 characters on mobile, so keep them concise.
Include your target keyword: This helps users quickly determine if the page matches their search intent. Google also bolds keywords (and their synonyms) that match the search query, which can boost clicks.
Use active voice: Active voice saves space and communicates your message more clearly.
Use Headings and Subheadings to Structure Your Page
H1 tags and subsequent headings make it easier for users to skim your page and help Google understand your page’s hierarchy.
Consider the following image.

Notice how difficult it is to read a page without organized headings compared to one that has them.
Headings also help Google grasp your page’s structure and assess if your content aligns with user search intent, which can boost your rankings for relevant keywords.
Incorporate keywords and variations in your headings to provide Google with more context about your page’s structure and content.
Use the H1 for your page title or headline, H2s for subtopics, and H3s, H4s, etc., for more detailed content.
Allocate sufficient time to develop high-quality content informed by thorough keyword research. Visitors are drawn to websites that fulfill their informational needs, underscoring the importance of crafting compelling content.
Search engines like Google assess the relevance and quality of website content to determine rankings for specific search queries. Therefore, prioritize creating informative, easily digestible content optimized with relevant keywords to resonate with your target audience.
Additionally, it’s imperative to address low-quality pages that may undermine your SEO efforts. Identifying and addressing thin content is essential for maintaining a robust online presence.
Regularly audit your website to identify and rectify any subpar pages, ensuring that your content remains optimized and beneficial for users and search engines alike.
Optimize URLs for Search Engine
Google advises using clear and concise URLs that are easy to understand.
Ensure your URLs contain words relevant to your content, avoiding cryptic numbers, dates, or sentences. Many website themes generate these automatically, so it’s essential to customize your URL before publishing.
Including your target keyword in the URL helps align it with your content’s topic.
An unfriendly URL may resemble a string of numbers or random characters, while an optimized URL is descriptive and user-friendly.
The more context Google has about a page through its URL, the better it can comprehend and match it with relevant search queries.
Strategically Add Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks within your website that direct users to different pages on the same site.
Here’s an example of what an internal link looks like on a webpage:

Internal links play a crucial role in on-page SEO optimization for the following reasons:
- They aid search engines in understanding your site’s structure and the relationships between pages.
- They enable Google crawlers to discover and navigate to new pages within your site.
- They indicate to Google that the linked-to page holds value.
- They enhance user navigation by guiding them through your website, thereby increasing user engagement and session duration.
Add External Links to Authoritative Sources
External links are links from your website that direct users to other websites. They play a crucial role in enhancing user experience and establishing credibility with your audience.
According to Google, incorporating links to authoritative external sources adds value to your users, contributing to a positive user experience.
To ensure effective external linking, consider the following best practices:
Only link to authoritative and reputable sites relevant to your topic and niche.
Use descriptive and natural anchor text to provide users with an idea of what to expect when they click.
Maintain a balanced number and placement of external links to avoid appearing spammy.
Include and Optimize Images
Incorporating images into your content enhances your potential to rank in Google Images, thereby driving more traffic to your site.
A fundamental step in image optimization is crafting descriptive alt text for each image.
Alt text, short for alternative text, serves two primary purposes:
- It provides context for search engine crawlers.
- It enables users with screen readers to receive descriptions of images.
Consider these tips for crafting effective alt text:
- Keep it concise: Screen readers truncate alt text after approximately 125 characters.
- Include a target keyword: Incorporating your target keyword provides context without keyword stuffing.
- Omit unnecessary phrases: Avoid redundant phrases like “image of” or “picture of,” as alt text inherently describes an image.
In addition to optimizing alt text, consider these image optimization strategies:
- Provide descriptive file names to assist search engines in understanding image content.
- Utilize Image compression tools to compress images for improved load times.
- Implement lazy loading to defer image loading until users scroll to them, enhancing page performance.
What Are Some Advanced On-Page SEO Techniques?
Once you’ve mastered the fundamentals of on-site SEO, you can explore more advanced techniques for optimizing your pages.
Let’s begin by addressing a critical on-page SEO element: page speed.
Optimize for Page Speed
While we may not have full insight into every Google ranking factor, page speed is a confirmed influencer.
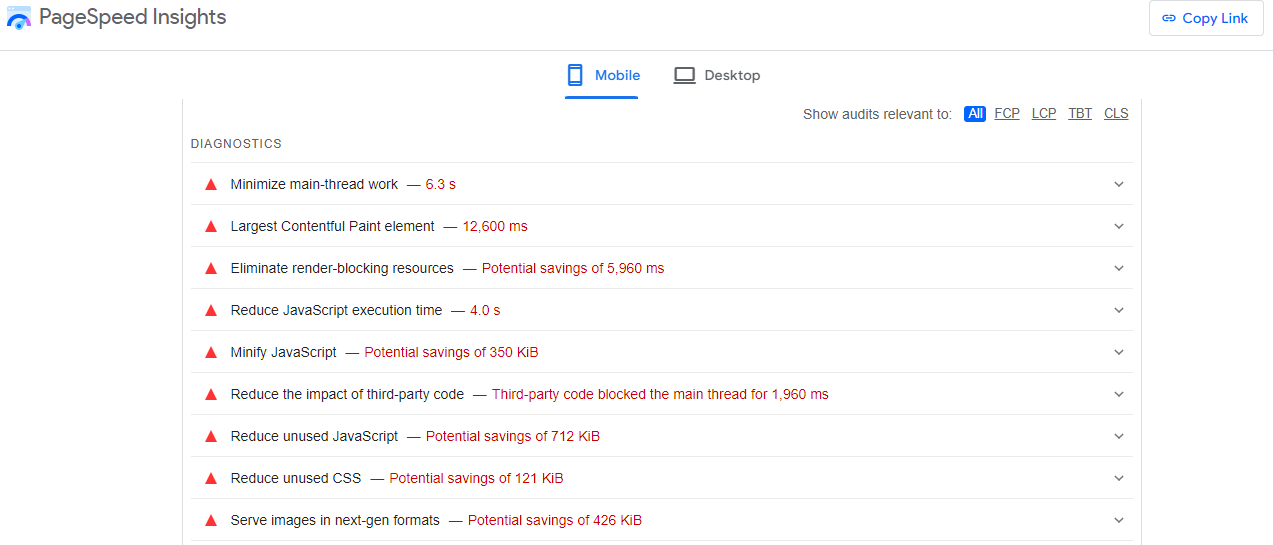
Optimizing for page speed is now more critical than ever. Utilize Google’s free PageSpeed Insights tool to evaluate overall performance scores for both mobile and desktop platforms, along with actionable suggestions for enhancement.
This tool evaluates Google’s Core Web Vitals, which encompass:
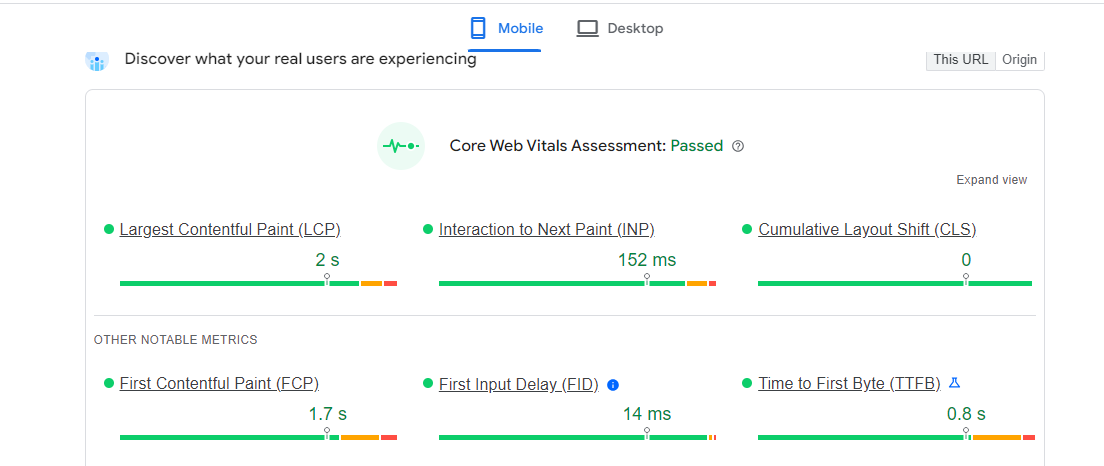
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time taken for the primary content to load.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Assesses the degree of webpage content shifting during loading.
The resulting report will provide valuable insights and highlight potential areas for improvement that may impact your site’s speed and overall performance.
Interaction to Next Paint(INP): Evaluates a webpage’s responsiveness using data from the Event Timing API. INP measures the latency of all user interactions on the page and provides a single value that most interactions fall under.
A low INP score indicates that the page consistently responds quickly to nearly all user interactions, enhancing the overall user experience.
First Input Delay (FID): Evaluates the time it takes for your website to respond to the initial user interaction.
To begin, input your URL and click the “Analyze” button.
These are all the errors that might be affecting your website’s speed and slowing it down:
Target the Featured Snippets
Featured snippets, positioned above organic search results as “position zero,” present an opportunity to enhance your click-through rate (CTR).
These snippets come in various forms, such as definitions, tables, lists, and videos. To secure the top spot, ensure your page adheres to on-page SEO best practices.
Strategies for targeting a featured snippet include:
- Providing concise, user-friendly answers to queries.
- Tailoring content to align with the user’s search intent.
- Formatting responses appropriately, whether through brief text, tables, videos, or other formats.
Add Schema Markup
Schema markup enhances search engine understanding of your website’s information by adding code that effectively communicates the page’s topic. This enables search engines to accurately interpret content, whether it pertains to an event, recipe, or other subjects, resulting in more informative SERP results.
Utilizing schema markup can generate rich snippets in the SERP, thereby occupying more prominent space and potentially improving your page’s organic click-through rate (CTR).
Here is a schema markup example which demonstrates recipe schema markup.
Various schema types can be applied to your pages, including reviews, products, events, people, and local businesses, among others. Detailed information on each type is available at Schema.org.
For instance, implementing “Event” schema markup can increase the likelihood of your events appearing prominently in search results, providing valuable details such as date, address, and location to Google. This enhanced visibility can lead to increased user engagement and traffic.
For further guidance on implementing Event structured data, refer to Google’s dedicated resource on the subject.
Write Main Content Above the Fold
When visitors arrive at your site from Google, they want quick answers.
Avoid huge images at the top of your page that delay access to content. Instead, prioritize placing your headline and introduction prominently.
While including an image at the start of your post is acceptable, make sure it doesn’t displace your content further down the page, hindering accessibility.
Reflect EEAT in your Content
Google’s guidelines for quality raters highlight the importance of displaying “EEAT” in content: expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
Although these guidelines don’t directly impact rankings, they offer valuable insights into the type of content Google favors in search results. Strengthen your EEAT by implementing the following strategies:
- Establish your relevant expertise within your author bio, particularly crucial for topics related to health, finance, and other YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) subjects.
- Incorporate quotes from recognized experts to enhance the credibility and authority of your content, especially in specialized fields where specific qualifications are essential.
- Deepen your understanding of the subject matter by immersing yourself in practical experiences. Whether it’s testing espresso machines or evaluating software, hands-on involvement adds authenticity to your content.
- Substantiate your expertise by providing evidence in your author bio and including original multimedia content, such as photos and videos, to illustrate your firsthand experiences and knowledge.
What Are Some Non-keyword-related factors that have an effect over on-page SEO?
In addition to the keywords utilized within webpage content and their context, various “keyword-agnostic” factors contribute to on-site optimization.
These factors encompass:
- Internal and External Links utilization: Consider the quantity and nature of links present on a page, including internal versus external links and their destinations.
- Page loading speed: Evaluate the time it takes for a page to fully load, as this directly impacts user experience.
- Implementation of structured data: Incorporating structured data enhances search engine understanding of webpage content.
- URL structure: Optimize page URLs to reflect content relevance and improve user navigation.
- Mobile compatibility: Ensure pages are optimized for mobile devices to accommodate diverse user preferences and behaviors.
- Page metadata: Craft informative metadata elements such as title tags and meta descriptions to accurately represent page content.
Ultimately, these elements collectively contribute to enhancing user experience, thereby facilitating improved on-site optimization performance.
Conclusion
Now that you have a grasp of what on-page SEO entails, it’s time to put your knowledge into action.
Implement the on-page SEO techniques discussed earlier, and you’ll set yourself on the path toward improved rankings and increased traffic. Remember, while on-page SEO can often lead to higher search result placements, the results may not be immediate.
Keep in mind that search results are dynamic and subject to change. Information evolves, as do user intents and search behaviors. Therefore, if you don’t see immediate improvements in your rankings, consider revisiting and refining your content.
By continuously updating and strengthening your content, you increase your chances of achieving better search engine visibility over time.





I’m extremely impressed along with your writing abilities and also with the layout
in your weblog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify
it your self? Anyway stay up the excellent quality writing, it’s uncommon to
see a great weblog like this one these days.
Snipfeed!
Thank you so much for your kind words! I truly appreciate it. Yes, I’ve created and customized everything myself—this is my own website. I’m glad you enjoyed the content and design!